TL;DR Science: Biofuel
By Eduard Shkulipa
September 29, 2021 · 4 minute read
Biology
Earth Science
Environmental Science
What is Biofuel?
Biofuel is a renewable fuel that is synthesized from organic material. Biofuels can be in solid, liquid and gas states, and their properties are similar to those of fossil fuels: they burn when they are ignited. That is why, compared to other forms of renewable fuels like electricity or hydrogen, biofuels require little to no adaptations in order to replace fossil fuels in everyday life. In fact, all Americans who fill their cars with petroleum or diesel already use biofuels, but more on that later.
Why Biofuels?
You might ask yourself: If we burn biofuels and they produce carbon dioxide just like fossil fuels, why are biofuels better?
That is a fair question. While it is true that burning biofuels produce carbon dioxide, it does not emit excessive gas to the environment, it rather “returns” carbon. The key difference is that biofuels are made from plants. Plants use energy from the sun and carbon dioxide in a process called photosynthesis to create sugars (the main product that the plant uses to grow) and oxygen (a byproduct of the reaction that happens to be necessary for us). That is why during the life of a plant, it takes carbon dioxide from the air. After the plant is transformed to fuel and burned, it releases the same amount of carbon dioxide to the environment without changing the level of gas in the air.
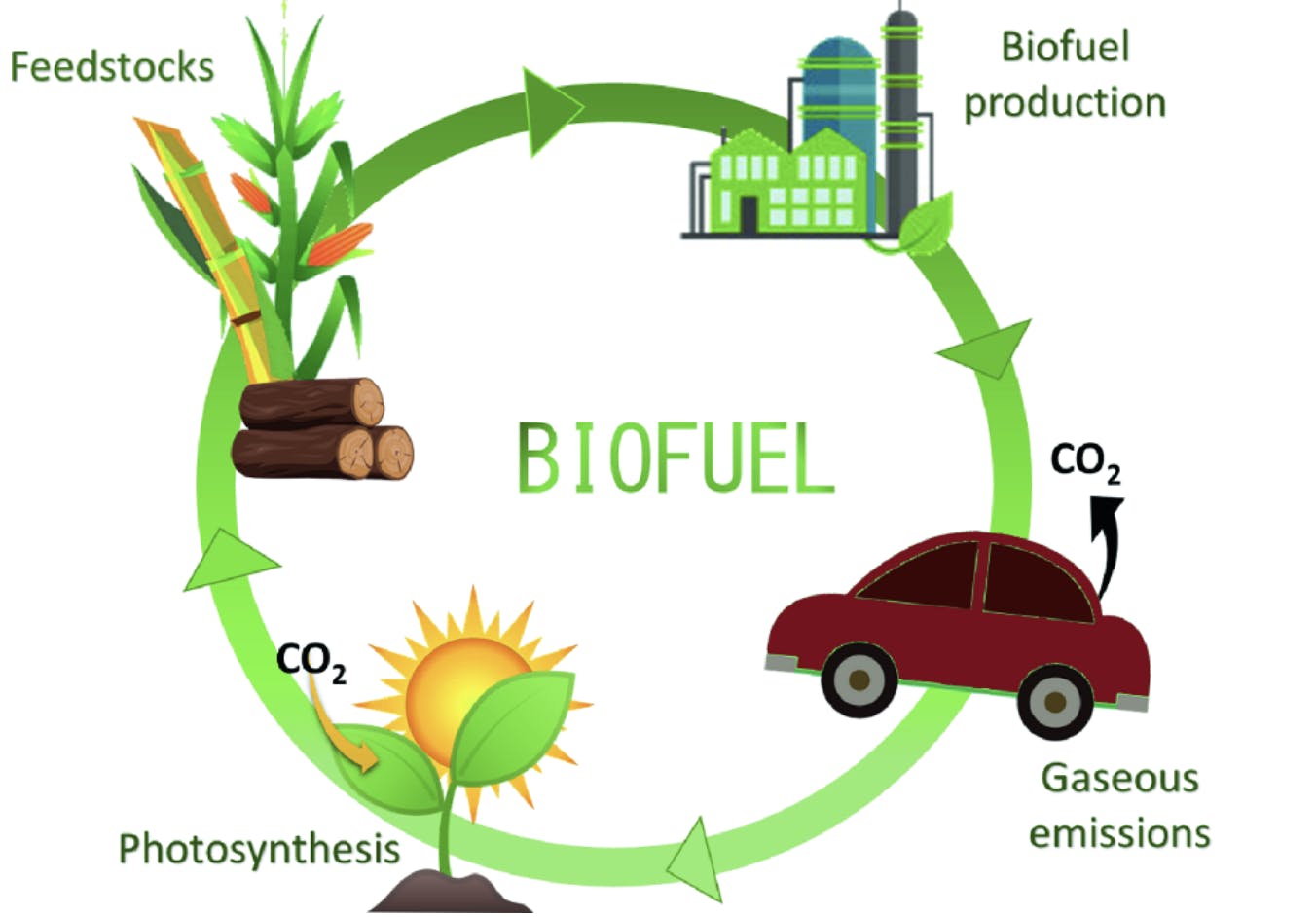
(Carbon cycle credit: Biofuels Production – Sustainability and Advances in Microbial Bioresources by Ajar Nath YadavAli Asghar RastegariNeelam YadavRajeeva Gaur)
Most Popular Biofuels
Nowadays the most used biofuels are wood, ethyl and biodiesel. It is fairly obvious how wood is made and used as a fuel, but not many people know how ethyl nor biodiesel are made and used.
Ethyl is a common alcohol, and it is created by using yeast and starch (in the form of shredded corn) in a reaction without oxygen. As a fuel, ethyl is mixed with common petroleum. Currently, all fuel in the U.S. has 10% ethyl in it. That way fuel is cheaper and cleaner in its production while its properties are the same.
Biodiesel is a fuel that is created by breaking down the natural fats’ (taken from any oily plant, usually for biodiesel, people use cooking oil or rapeseed’s oil) cell structure, typically with heat, and then transforming the substance into flammable fuel with chemicals. Biodiesel can and is used as a fuel for cars all over the world in its pure form, although it is more often sold mixed with regular diesel.
Drawbacks of Biofuels
While biofuels have several advantages, they still have drawbacks.
First of all, biofuels are not as energy efficient as fossil fuels. That is why they are rarely used in their pure form but rather mixed with fossil fuels. Also, a lot of arable land is reserved for the production of biofuels, limiting the area of production of food which is necessary for our survival. In the last year, almost 12% of agricultural land was dedicated to growing plants for biofuels.
This brings another problem: destruction of land. With erosion of land, deforestation, and fresh water over usage, we harm the environment. This could outweigh the benefits biofuels offer and cause more harm.
Solutions
However, there are solutions for each of these problems.
People are aware of these problems, companies are investing in research, and scientists are working on solving them. For example, ExxonMobil, an oil company, has invested more than $300 million in biofuel research over the last decade. On this ground, many new researches have appeared that provide alternatives for current biofuels. One of the most prospective research held in the Field Test Laboratory Building (FTLB) at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in Golden, Colorado, is experimenting on algae based biofuel. Algae could be grown on depleted lands using dirty water that could not be used elsewhere; also, containing more fat, algae fuel is more energy efficient.
TL;DR
Biofuel is a renewable fuel made from plants that could replace fossil fuels. While growing, plants consume carbon dioxide. After they are transformed to biofuels and burned, they release the same amount of carbon dioxide, creating a cycle of carbon. The most popular biofuels are ethyl and biodiesel, and they are already in use all over the world.
Even though biofuels have drawbacks, a lot of researchers are dedicated to improving this fuel and making it safer for the environment.
Sources
-https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/biofuel.asp
-https://www.energy.gov/eere/bioenergy/biofuel-basics
-https://www.britannica.com/technology/biofuel
-https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/biofuel
-https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OpEB6hCpIGM&ab_channel=RealEngineering
Did you enjoy this article?
About The Author
Eduard is a freshman at University of California San Diego. He enjoys engineering, math, solving Rubick’s cubes, swimming, and, strangely enough, collecting coins. Send him a question or suggestion at eduard@sciteens.org.