TL;DR Science: Oncogenes
By Thomas P.
June 17, 2022 · 3 minute read
Biology
Medicine
Chemistry
Perhaps you may have heard someone say at one point “I am at risk for ___ cancer, so I have to take extra precautions…”. Or, you may have heard the claim that “Sunscreen can reduce your risk of getting skin cancer”. Two questions consequently arise: first, how do we actually know of cancer risk; second, what does it mean to be at risk? To start we have to look at our cells’ DNA and what can happen if it becomes mutated.
Our cells’ DNA
Every cell in our body has 23 pairs of chromosomes, each pair coming from your father and mother. In theory, each cell is supposed to have the same DNA. Remember that DNA is supposed to provide instructions for all bodily processes that would be performed by a cell (basically everything).
Mutations (insertion, deletion, or inversion of a nucleotide bases) can form in cell DNA as a result of natural processes, such as exposure to UV light or exposure to certain substances called carcinogens (this is called an acquired mutation). Most mutations are benign (have no effect), but some are malignant. In addition, a mutation can also come as a result of inheritance (within the sperm/egg) (this is called a germline mutation).
Mutations and cancer/oncogenes
So, what do cell mutations have to do with cancer? And what are oncogenes (the topic of this article)? By definition, oncogenes are genes that cause cancer because they lead to the uncontrolled proliferation of cancer cells (creation of a tumor).
The answer to the former question, however, lies in proto-oncogenes. Proto-oncogenes, by definition, are genes that if mutated or overexpressed (instruct too much) could lead to cancer. Typically, such genes are associated with those that control cell growth. However, mutations in genes associated with cell death (called tumor suppressor genes*) and DNA repair genes** can also lead to cancer.
Upon a proto-oncogene being mutated, it turns into an oncogene and has the potential to cause a tumor if it leads to cells growing and reproducing uncontrollably, if it is not kept in check by the tumor suppressor genes or the DNA repair genes.
—-------
*Genes associated with apoptosis (cell death) and prevent the uncontrolled proliferation and growth of cells. Whereas oncogenes cause cancer, tumor suppressor genes prevent it.
**Genes that provide instruction on how to fix DNA mutations.
—--------
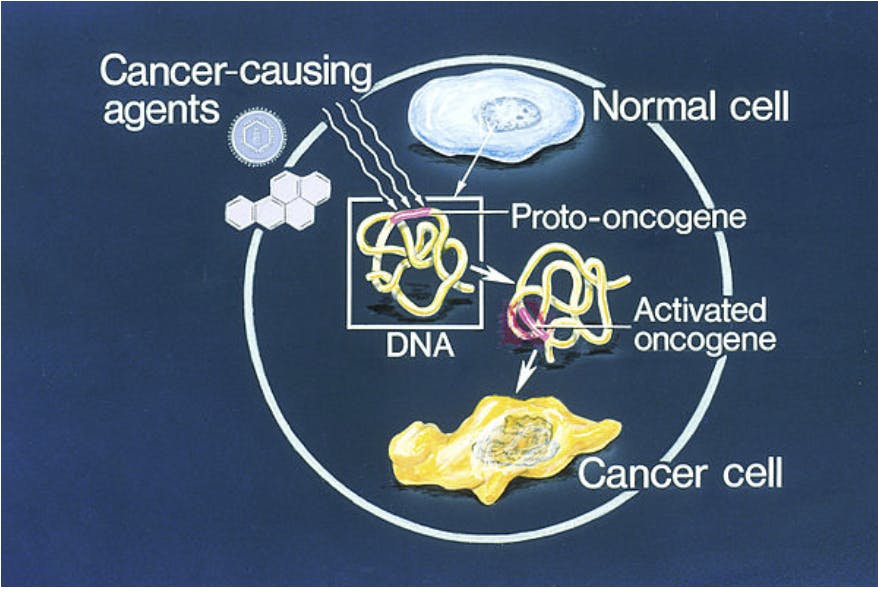
From proto-oncogene to cancer.
Preventative measures
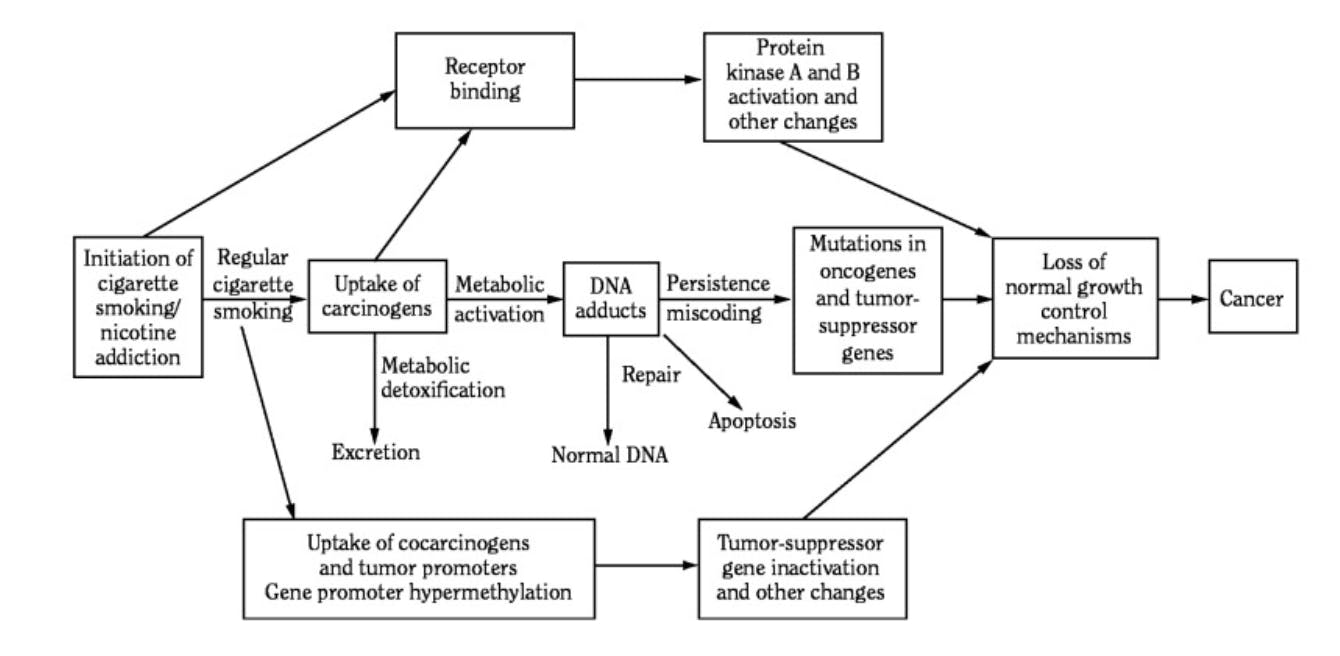
We take steps everyday to reduce our risk of cancer. These precautions include using sunscreen, which block UV rays that can damage our DNA causing subsequent mutations when replicated. In addition, most people are also wary of carcinogens, items that increase cancer risk by causing an increase in DNA mutations. For example, smoking contains numerous carcinogens, which all collectively cause persistent DNA mutations in tumor suppressor genes*, DNA repair genes**, and oncogenes.
The following image details how smoking causes lung cancer. Regular cigarette smoking causes an uptake of carcinogens, which can bind to DNA unless repaired (DNA adducts and receptor binding); this eventually causes mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, which have the potential to cause cancer.
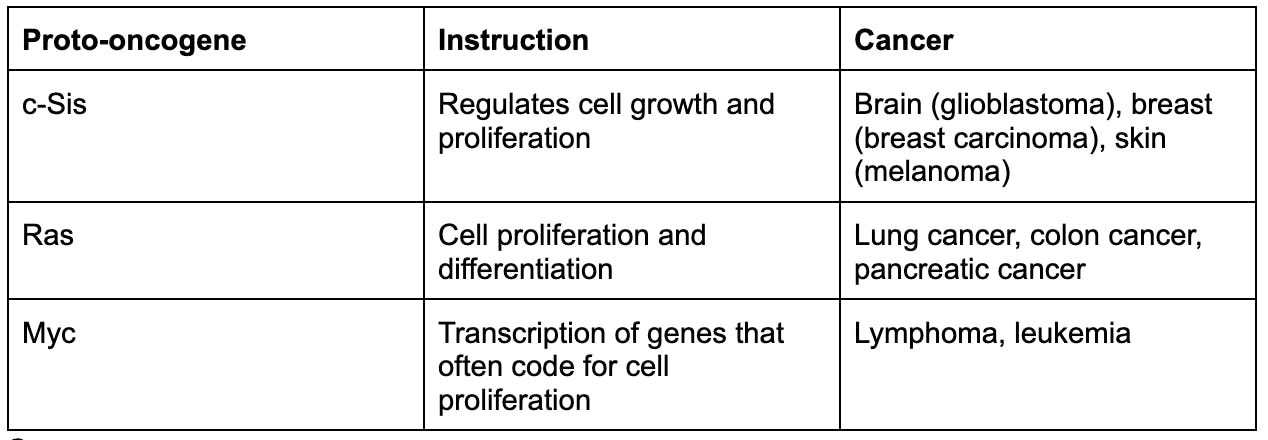
Examples of (proto-)oncogenes
Sources
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=85&contentid=p07205
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oncogene
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9840/
https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/proto-oncogenes-to-oncogenes-to-cancer-883/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53010/
https://www.news-medical.net/health/C-Sis-Proto-Oncogene.aspx
Did you enjoy this article?
About The Author
Thomas is a student at Eastside High School.