TL;DR Science: Enzymes in the Human Body
By Srishti S.
November 04, 2022 · 2 minute read
Medicine
Biology
Replicating DNA, building muscle, even turning food into energy – these processes are all made possible by enzymes. These substances work from head to toe to keep the human body up and running. But what are these “enzymes”, and how do they help us?
What is an Enzyme?
An enzyme is what we call a biological catalyst, or a substance that speeds up chemical reactions. Enzymes do just that: they speed up processes in the body in a specific way. Let’s take a look at how these proteins work.
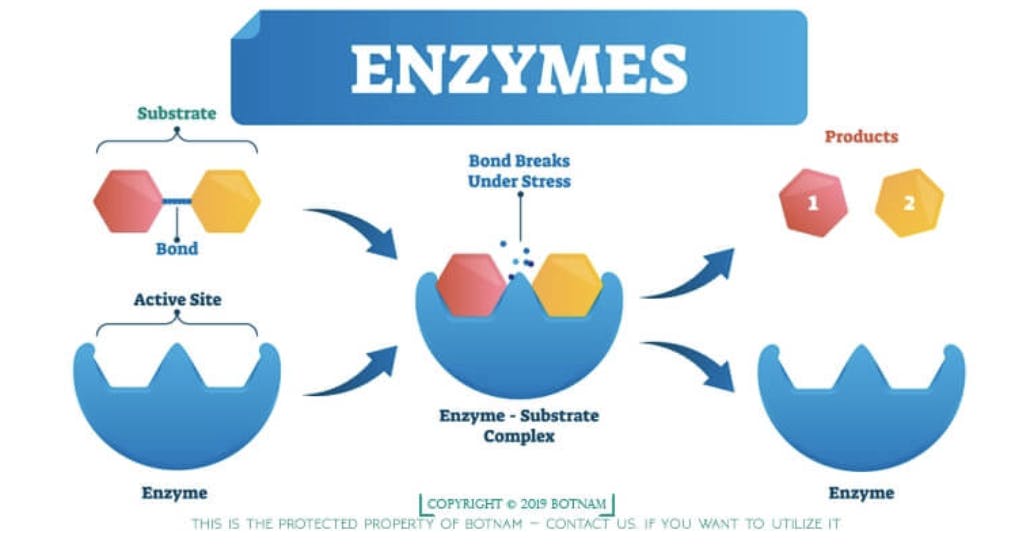
The Basics
To understand the process of catalyzing reactions, we first need to talk about activation energy. Every chemical reaction requires a certain amount of activation energy to get it started. The higher the amount of activation energy needed, the slower the reaction will be. Enzymes shorten this process by lowering the amount of activation energy required to initiate a reaction.
Enzymes, Substrates, and Products
There are thousands of different enzymes in the human body; that’s because certain enzymes can only work on certain substances. The substance that an enzyme acts on is called the substrate of the reaction. This substrate is also known as the reactant, or the substance before the chemical reaction. For example, the enzyme sucrase breaks down the substrate/reactant sucrose. The products are what come out of the reaction. So, the enzyme breaks down the sucrose into the products glucose and fructose.
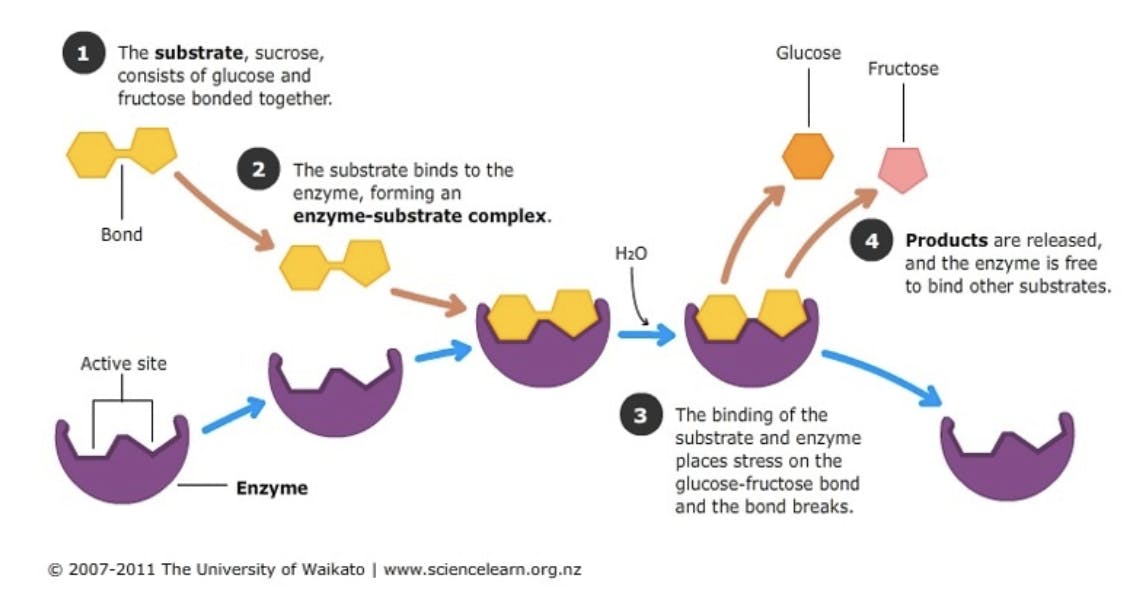
Enzymes and substrates fit together like puzzle pieces. The place where the two connect is called the active site of the enzyme (where the reaction begins). The shape of this active site is unique to each enzyme; only specific substrates can fit, and only the corresponding reactions can occur. Once an enzyme catalyzes a reaction, it doesn’t change or reduce in size; it can be reused over and over again! However, factors like pH or changes in bodily temperatures can denature the enzyme, or render it useless. That’s why it is so important to keep conditions within the body stable; it’s the only way enzymes can do their job!
Examples in the Human Body
Reactants: Red Products: Blue
Key: red is bolded and blue is italicized and bolded
- The liver enzyme catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
- The enzyme lipase breaks down triglycerides (fats in the body) into fatty acids and glycerol.
- The small intestine enzyme lactase breaks down lactose into the sugars glucose and galactose.
undefined - The enzyme amylase (found in saliva) breaks down starches into maltose and other substances.
***All of these enzymes are used to speed up the process of breaking down the substances listed above.
TL;DR
The human body is a complex system that can do numerous things at once, but we sometimes don't appreciate what makes everything happen behind the scenes. Even the smallest of substances can play a big role in keeping the body functioning and well. Enzymes are at the forefront, speeding up processes we may not even know about! Every time you exercise, eat, or even breathe, there is an enzyme at play!
Here is a great video about enzymes if you want to learn more!
Sources:
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319704
https://www.healthline.com/health/why-are-enzymes-important
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/21532-enzymes
https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Enzyme
Image Sources:
https://botnam.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Enzymes-are-proteins.jpg
https://news.mit.edu/2018/scientists-deliver-high-resolution-glimpse-enzyme-structure-0220
Did you enjoy this article?
About The Author
Srishti Swaminathan is a high school sophomore interested in STEM and writing. She enjoys reading, listening to music, and watching movies. If you have any comments or questions regarding this article, feel free to contact her at srishti@sciteens.org.