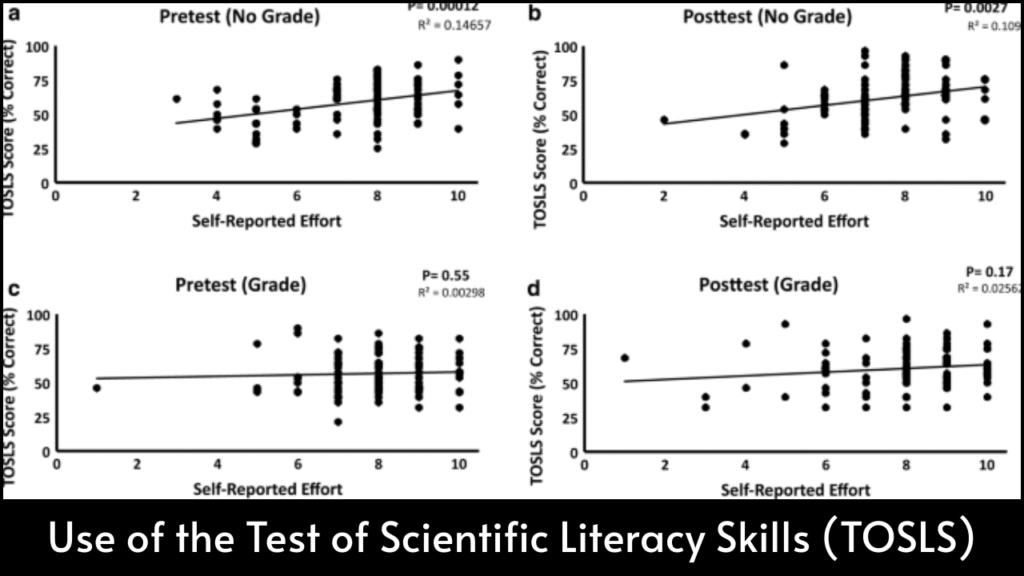
Scientific literacy stands as an essential ability in the modern world, where individuals continuously interact with scientific information. The Test of Scientific Literacy Skills (TOSLS) is a structured tool created to measure how well people understand, interpret, and apply scientific information in real-world contexts. Education systems, research communities, and policymakers use TOSLS to evaluate not just academic knowledge but the capacity to make reasoned decisions in daily life based on evidence. An examination of its use highlights its value in classrooms, research, public policy, and lifelong learning.
Table of Contents
Overview
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Test of Scientific Literacy Skills (TOSLS) |
| Purpose | To assess individuals’ scientific reasoning, critical thinking, and ability to interpret scientific data |
| Primary Users | Educators, researchers, curriculum designers, policymakers |
| Target Audience | University students, high school learners, and the general public in literacy studies |
| Format | Multiple-choice questions focused on real-world applications |
| Skills Measured | Interpretation of graphs, understanding of scientific arguments, evaluation of data reliability, and decision-making using evidence |
| Outcome | Provides insights into the effectiveness of teaching strategies and learners’ scientific understanding |
Importance of TOSLS in Education
- Learning Assessment
- TOSLS helps instructors evaluate whether students can apply scientific knowledge beyond textbook learning.
- It highlights gaps in critical thinking and comprehension.
- Curriculum Development
- Results guide educators in redesigning courses to strengthen reasoning and analysis.
- Focus shifts from rote memorization to problem-solving.
- Skill Transfer
- Students learn to transfer classroom knowledge to real-world contexts, such as environmental issues, healthcare choices, or technological debates.
- Equity in Education
- TOSLS provides standardized measurement, allowing fair comparison across diverse learning environments.
Applications of TOSLS
- University Classrooms
- Widely used in introductory science courses to determine baseline literacy levels.
- Professors adapt teaching methods based on results.
- Research Studies
- Provides consistent measurement tools for academic studies on education.
- Researchers compare scientific literacy levels across demographics, countries, or teaching methods.
- Policy Evaluation
- Policymakers use data to assess the effectiveness of education reforms.
- Helps determine if public education goals in science literacy are being met.
- Public Engagement
- Literacy skills measured by TOSLS extend into public decision-making, such as health awareness or climate change understanding.
Skills Evaluated by TOSLS
| Skill Area | Description | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|
| Data Interpretation | Reading graphs, charts, and figures | Understanding COVID-19 infection rate charts |
| Argument Evaluation | Identifying the strength of evidence in claims | Evaluating news reports on climate change |
| Critical Thinking | Differentiating between fact and opinion | Judging the reliability of online medical advice |
| Problem Solving | Applying scientific reasoning to situations | Deciding the best recycling practices |
| Evidence-Based Decision Making | Making choices supported by data | Choosing energy-efficient appliances |
Advantages of Using TOSLS
- Standardization
- Provides a uniform benchmark across institutions.
- Practical Relevance
- Focuses on applied skills rather than memorized facts.
- Versatility
- Can be adapted for different education levels and settings.
- Improved Teaching
- Feedback from results enhances instructor strategies.
- Promotion of Lifelong Learning
- Encourages learners to apply scientific reasoning in everyday life.
Challenges in Using TOSLS
- Cultural Differences
- Some questions may reflect biases toward specific contexts.
- Language Barriers
- Learners with weaker English proficiency may struggle even if scientifically capable.
- Over-Reliance on Tests
- Scientific literacy includes skills beyond testable items, such as creativity and collaboration.
- Need for Continuous Update
- Scientific contexts evolve, requiring regular revision of questions.
Role in Improving Education
- Evidence for Teaching Methods
- TOSLS identifies whether active learning strategies, group discussions, or lab-based teaching improve literacy more effectively than lectures.
- Motivation for Students
- Learners gain awareness of their critical thinking progress.
- Global Comparisons
- Enables international collaborations in education research by providing comparable data.
- Alignment with Competency-Based Learning
- Matches global education trends that emphasize skills over rote learning.
Case Examples of Use
- Undergraduate Programs
- Science faculties in universities apply TOSLS at the start and end of courses to measure growth.
- STEM Outreach Programs
- Community workshops use TOSLS to evaluate how well non-scientists understand issues like renewable energy.
- Teacher Training
- Teacher education institutions employ TOSLS to prepare future educators in fostering scientific literacy among school students.
- Cross-Disciplinary Research
- Social science and medical studies use TOSLS to examine literacy connections with decision-making on public health.
Comparison with Other Assessment Tools
| Feature | TOSLS | Concept Inventories | Standard Exams |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Real-world literacy skills | Conceptual understanding of scientific principles | Knowledge recall |
| Format | Application-based multiple-choice | Discipline-specific tests | General curriculum-based |
| Use | Broad, across disciplines | Limited to physics, chemistry, etc. | Standard academic assessment |
| Outcome | Evaluates reasoning and critical analysis | Measures conceptual mastery | Provides grades or ranks |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to new contexts | Fixed by discipline | Limited adaptability |
Future Directions of TOSLS
- Integration with Digital Platforms
- Online testing methods can provide immediate feedback.
- Adaptive Questioning
- Use of artificial intelligence could tailor difficulty levels to learners.
- Cross-Cultural Expansion
- Translation and localization will make it suitable for diverse populations.
- Connection with Real-Life Data Sources
- Future tests may include interactive datasets or simulations.
- Use in Workforce Training
- Companies may apply TOSLS to ensure employees understand technological and environmental issues relevant to industries.
Other Important Information
- Reliability and Validity
- Studies confirm strong reliability across different learner populations.
- Accessibility
- It can be adapted for students with disabilities by modifying question presentation.
- Time Requirement
- Designed to be completed in less than an hour, making it practical.
- Scalability
- Suitable for large classroom settings and research with thousands of participants.
Key Takeaways
Scientific literacy determines how individuals interpret, evaluate, and use scientific information in daily life. The Test of Scientific Literacy Skills (TOSLS) plays a vital role by offering a structured, reliable way of measuring this ability across diverse learners and settings. Education systems, policymakers, and researchers benefit from its use in assessing teaching methods, guiding reforms, and preparing societies for scientifically informed decision-making. Broader adoption and continuous refinement of TOSLS will ensure that future generations possess the necessary tools to engage meaningfully with science in an increasingly complex world.