SciTeens’ Ampere News: 5 Cool Current Science Events From This June
By Grace Jiang
June 30, 2021 · 6 minute read
Welcome back to SciTeens’ Ampere News! At the end of each month, we publish an article highlighting some interesting developments in the world of science over the last thirty(ish) days. For today's edition, we'll provide a summary of science news from June.
For those curious as to why we named the series Ampere, the ampere is the standard unit of measurement of electrical current. Likewise, we hope that SciTeens will become the standard for keeping up with the most interesting and current news in STEM! The following infographic summarizes what we have in store for this month; feel free to scroll through and jump right to which story seems the most interesting to you!

1. NASA plans to send spacecraft to Venus
What happened?
On June 2nd, NASA selected its next two missions to Venus, named DAVINCI+ and VERITAS. These missions vere chosen based on their “potential scientific value and the feasibility of their development plans.” NASA awarded ~$500 million to each mission, and the two project teams are now finalizing development plans. Launch is scheduled for sometime between 2028 and 2030.
Why did it happen?
Venus is known as Earth’s “twin” due to their similar size, density and relative proximity in the solar system. Yet, the conditions on Earth and Venus are so different that they could almost be considered opposites (for example, Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system due to its heat-trapping atmosphere). Venus is therefore an unlikely place for life. However, evidence suggests that it was once covered in water. Scientists are curious at how Venus and Earth, two planets that appear so similar on the surface, turned out to be so different over the past few billion years.
DACINCI+ will send a probe into the atmosphere of Venus to analyze gas composition, and VERITAS will orbit Venus to take pictures and make 3-D maps—both to figure out how the planet became what it is today.
Why does this matter?
No NASA mission has visited Venus in more than 30 years; if successful, the DAVINCI+ and VERITAS missions will certainly make their mark in history. More information will likely be out about this mission in the coming years.
2. Scientists prove how auroras form
What happened?
Auroras are beautiful displays of light that fill the night sky. A well-known example is the aurora borealis, or northern lights (shown in the photo below).
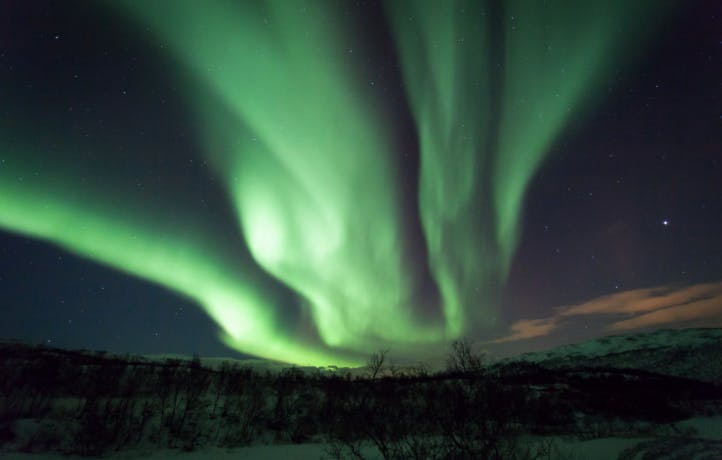

Auroras form when electrons (tiny negatively charged particles) from outer space collide with oxygen and nitrogen atoms in the atmosphere. Normally, Earth’s magnetic field blocks these electrons, but there is a region of the atmosphere (known as the ionosphere) surrounding the north and south poles that allows in a relatively large amount of electrons.
Before, nobody knew how exactly electrons from space were able to come near the ionosphere in the first place. Scientists had suspected that these electrons were pushed in through Alfvén waves, ripples along magnetic field lines that spacecraft have identified as existing in space. In an article published on June 7th, researchers conducted an experiment that proves this phenomenon.
How did it happen?
The conditions in a large tube-shaped chamber were made to mimic those of Earth’s atmosphere. Scientists first filled the tube with plasma, a mixture of positively and negatively charged particles often referred to as the “fourth state of matter” (solid, liquid, and gas are the other three). A magnetic field, created by electrical coils, also ran through the chamber.
The scientists then placed an antenna to generate Alfvén waves through the tube, and electrons in the plasma were pushed down the chamber by the resulting waves. This proved that Alfvén waves do indeed push electrons into the Earth’s atmosphere to generate auroras.
Why does this matter?
Auroras are a natural phenomenon, yet they almost seem supernatural. A brilliant, colorful glow spreading across a large expanse of the sky—this would certainly look like magic to the regular person. Scientists have had theories for how these magical displays of light are formed, but with this experiment, they finally have proof.
3. Makeup products shown to contain dangerous ‘forever chemicals’
What happened?
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are also known as “forever chemicals” because they don’t break down over time, accumulating in the body and the environment. Although not much is known about their exact toxicity, evidence does connect PFAS exposure to negative health impacts.
In a report published on June 15th, scientists screened a large variety of cosmetics and discovered PFAS presence in a majority of the products.
How did it happen?
From stores in the U.S. and Canada, 231 cosmetic products were purchased. Scientists screened these products for fluorine content using a technique called particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy. As PFAS are made of chains of carbon and fluorine atoms, high fluorine content would indicate presence of PFAS compounds. The scientists found 52% of the tested products to contain high concentrations of fluorine.
Why does this matter?
This is the first large screening of cosmetics for PFAS, and it showed that an alarmingly large portion of makeup products contain these potentially harmful compounds. Although the specific health risks of PFAS in cosmetics are not known, PFAS have been linked to adverse health effects in humans. More research will need to be conducted to determine the exact significance of the findings of this study.
4. Geckos provide insight into skin cancer
What happened?
The “Lemon Frost” variety of leopard gecko emerged around 2015 from selective breeding and spontaneous mutation. Lemon Frost geckos have special skin coloring that makes them distinct from the many other leopard gecko varieties. It also has skin that tends to develop tumors more frequently than other varieties of gecko.
In a paper published on June 24th, researchers study tumor formation in Lemon Frost geckos. They trace both Lemon Frost tumor formation and coloring to a mutation on the same gene, SPINT1.
How did it happen?
The researchers collected DNA from the saliva of ~30 Lemon Frost geckos who had two Lemon Frost parents, ~100 Lemon Frost geckos who had one Lemon Frost parent, and ~40 non-Lemon Frost geckos. The DNA was sequenced and analyzed, and the SPINT1 gene was determined to be a strong candidate for the Lemon Frost skin coloring. With this Lemon Frost coloring also came the increased risk for skin tumors for the geckos.
Why does this matter?
The SPINT1 gene has also been linked to cancer in humans and tumor formation in fish and mice. In the Lemon Frost geckos, the gene plays a role in skin coloring by causing overproduction of white skin cells. This gives the geckos both their “frosted” appearance and a higher susceptibility to tumors. Future studies on the Lemon Frost geckos and the SPINT1 gene may lead to breakthroughs in cancer research.
5. Paleontologists examine skull of human species closely related to modern-day humans
What happened?
In a paper published on June 25th, paleontologists describe a skull belonging to a now-extinct member of the human family. They call the species Homo longi, or “Dragon Man,” and claim this new species replaces Neanderthals as the closest relative of modern-day humans.
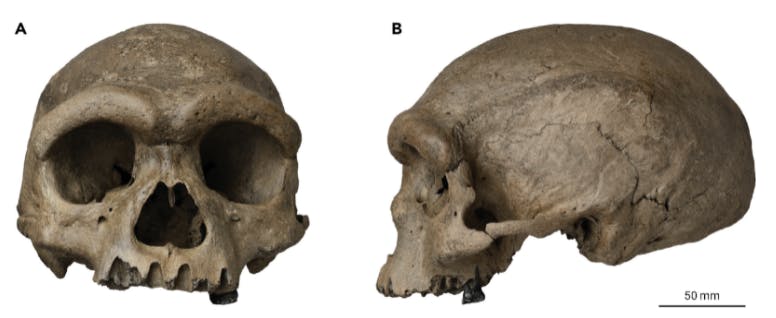
Ni et al./The Innovation 2021
How did it happen?
Around 90 years ago, when Japanese soldiers were occupying northern China, a Chinese man found a human skull in a riverbank. He had placed the skull in a well to hide it from his Japanese supervisors. Now, the skull has come out of hiding, allowing scientists to examine it in detail and hopefully classify it.
Why does this matter?
Although the scientists in the paper claim that the discovered skull belongs to a closer relative to humans than Neanderthals, other researchers are skeptical. Many other scientists believe that the skull, in reality, belongs to the Denisovans, another ancestor closely related to modern-day humans, though less related than the Neanderthals. However, if the skull is indeed a Denisovan skull, it would be the first Denisovan skull to be found, finally giving a face to the mysterious species.
Wrapping Up:
- NASA plans to send two missions to Venus, DAVINCI+ and VERITAS, both scheduled to launch between 2028 and 2030
- Scientists prove through experiment that Alfvén waves sweep electrons into Earth’s atmosphere to form auroras
- Scientists test cosmetic products for harmful PFAS compounds (“forever chemicals”) and find PFAS presence in 52% of the products
- Tumor formation in Lemon Frost geckos is tied back to a mutation in the SPINT1 gene
- Some paleontologists classify new human skull as belonging to the Denisovans; others classify it as a species more closely related to humans than Neanderthals
Did you enjoy this article?
About The Author
Grace Jiang is currently a senior at Pine View School. She loves many things, the most notable of which being ice cream, harp seals, bubble tea, and (of course!) science. Definitely go contact her at grace@sciteens.org if you have any future article recommendations or just want to discuss life.