TL;DR Science: Electric Vehicles
By Thomas P.
March 31, 2021 · 3 minute read
Chemistry
Earth Science
Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
Environmental Science
If anything has changed the automotive industry the most, it is most certainly electric vehicles (EVs for short). However, there are currently many misconceptions about this new technology. This week’s article will discuss how all-electric vehicles work, how they are different from cars that are fueled by traditional gas-burning internal combustion engines (ICE for short), and some critical connections between the use of electric cars and combating climate change.
How do Electric Vehicles work?
It may seem pretty obvious as to how electric cars are different from ICE cars in terms of how they work. However, the difference in how they work is much larger than just having to have “plug in your car”.
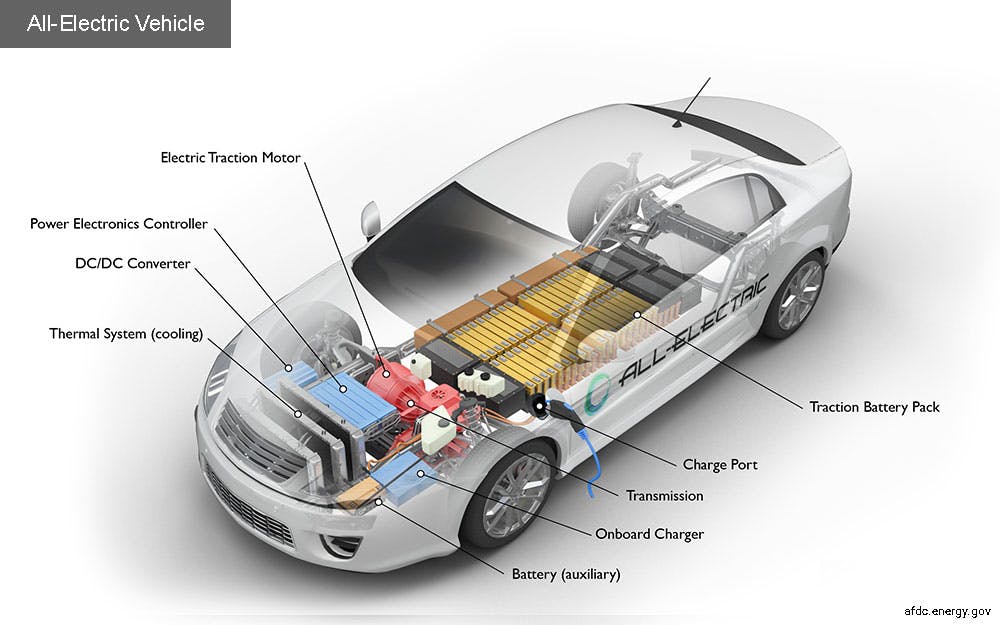
Electric cars have different car parts compared to ICE cars, as their power does not come from an engine but rather from a traction battery pack and electric motor. Instead of using up gasoline, the traction battery pack and electric motor can be recharged from the car's charge port. The best all-electric cars have battery packs called Lithium-Ion batteries, which involve the use of the elements: Lithium, Nickel, and Cadmium. Because an electric car does not have a giant engine that it needs to fit in the front of the car under the hood, there is more storage room in these cars. Because much of the energy stored in a Lithium-Ion battery that is transferred to an electric motor is not being lost due to heat, as is the case with the ICE engine, the electric motor is much more efficient than the ICE engine. In fact, engines only convert 12-30% of all energy in gasoline to power the wheels, while electric cars convert more than 77% of all energy in order to power the wheels.
Range of Electric Cars
Certain people who are unfamiliar with electric cars have the tendency to lament about them not having optimal range (ie. driving distance), and their need to be charged often. However, this only applies to certain early electric cars whose batteries were too small. For instance, a Tesla Model 3 does not have the same range as a Nissan Leaf by virtue that the Nissan Leaf has a much smaller battery than the Tesla. However, all the electric vehicles currently available for sale in the U.S. market are able to handle the needs of most daily commuters (commuter distances average 37 miles per day).
Take a look at the cars side-by-side:


Implications of Electric Vehicles
While Electric Vehicles are able to drive without polluting the air with Carbon Dioxide, they still do pollute, just in a different way. Because electric cars sometimes have their electricity sourced from a coal or natural gas power plant (at least in the U.S), they are still using electricity generated from fossil fuels. Some greenhouse gasses are also generated by the manufacturing of electric vehicles. In fact, a recent Wall Street Journal article states that electric vehicles generate more greenhouse gases as a result of their complex manufacturing when compared to ICE vehicles.
Besides the production of EVs, each time we need to charge our electric vehicle, we need electricity. Where does this power come from? Well at the moment, mainly coal and gas power plants. However, as more and more power plants transition to renewable energy, the production of electricity will less greenhouse gas. As a result, though electric cars still do indirectly pollute, they are expected to become cleaner over time. These benefits for electric vehicles make them a viable option to combat climate change in the long run. In fact, President Biden has pledged to soon make the U.S. government fleet all-electric, though the date that it will take effect is not yet set in stone. In addition, the state of California has also mandated that in 2035 all newly sold cars be fully-electric.
TL;DR
Electric Vehicles run on a Lithium-Ion battery that can be recharged with electricity, creating less pollution than a traditional gas-powered engine. While current EVs are sometimes limited by the distance they can travel on a single charge, newer models of electric cars have the ability to travel distances comparable to their traditional gasoline-fueled counterparts. Electric Vehicles are proven to produce less pollution in the form of nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and other pollutants than traditional cars and EVs may play a key role in combatting climate change in the decades to come.
References:
https://www.ucsusa.org/resources/how-do-battery-electric-cars-work
https://www.cei.washington.edu/education/science-of-solar/battery-technology/
https://afdc.energy.gov/vehicles/how-do-all-electric-cars-work
https://www.caranddriver.com/features/a27127697/plug-in-hybrid-2019/
https://www.fueleconomy.gov/feg/evtech.shtml
https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/ohim/onh00/bar8.htm (Note: source states miles driven per year)
https://www.wsj.com/graphics/are-electric-cars-really-better-for-the-environment/ (paywalled)
Did you enjoy this article?
About The Author
Thomas is a student at Eastside High School.